
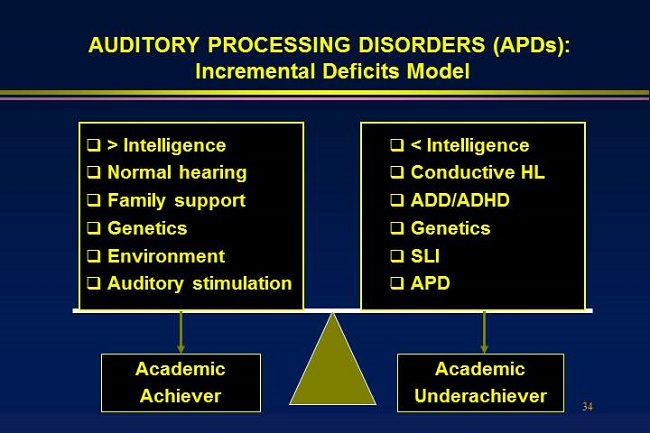

Mild symmetrical hearing loss is present, but client shows difficulty hearing in noise beyond that typical for someone with such a level of hearing loss.Hearing is normal and symmetrical, but Word Discrimination scores are asymmetrical (more than a 10% difference).Hearing is “within normal limits” (per audiogram) and Word Discrimination is above 88% in a quiet environment.(In severe cases, some testing can be done at age five.) Hearing : When to Refer for (C)APD Testingīy Laura Polich, Ph.D, CCC of Portland Auditory Processing DiagnosticsĬhildren or adults merit consideration for (Central) Auditory Processing testing if some or all of the characteristics below are present:ĪGE: Child is seven years of age or older. Non-modality-specific cognitive processing and language problems may manifest themselves in auditory tasks (i.e., as listening problems) however, diagnosis of (C)APD requires demonstration of a deficit in the neural processing of auditory stimuli that is not due to higher order language, cognitive, or related factors. (Central) auditory processing disorder (C)APD refers to difficulties in the processing of auditory information in the central nervous system (CNS) as demonstrated by poor performance in one or more of the following skills: sound localization and lateralization auditory discrimination auditory pattern recognition temporal aspects of audition, including temporal integration, temporal discrimination (e.g., temporal gap detection), temporal ordering, and temporal masking auditory performance in competing acoustic signals (including dichotic listening) and auditory performance with degraded acoustic signals. ASHA’s ( Definition for Auditory Processing:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
